

If you’re reading this, it’s probably because you’re aware that it’s more expensive to acquire a new customer than it is to retain an existing one, or that an increase in customer retention can produce an increase in profit. If either of those things are true, you’ve come to the right place.
In this blog post, we’ll cover everything you need to know about upselling and cross-selling — two sales techniques designed to generate more revenue from your existing customer base — including what they are, best practices, industry examples, and more.
Upselling vs. Cross-selling: What’s the Difference?
Upselling and cross-selling are sales strategies that aim to convince the buyer to spend more money than they originally intended. Pretty simple, right? Let’s break it down in a little more detail.
With upselling, the seller encourages the buyer to purchase an upgrade, an add-on, or the premium version of a product.
For example, let’s say that you run a software company that sells products using a monthly subscription model. While reviewing your existing customer base — let’s say a total of 10,000 subscribers — a member of your sales team notices that one customer is subscribed to the basic version of your main product at $50 a month. The representative approaches that customer and suggests that, for an additional $10 a month, they could upgrade to premium version and gain access to a wider feature set. The customer agrees to the upgrade, resulting in an additional $120 in revenue for every year they remain a subscriber. Now, let’s say that half of your existing customer base — that’s 5,000 subscribers — uses the basic version of your main product. If your sales team is able to convince even one in every five of those basic-level customers to upgrade their subscription to the premium version, you’re looking at an additional $120,000 in revenue per year.
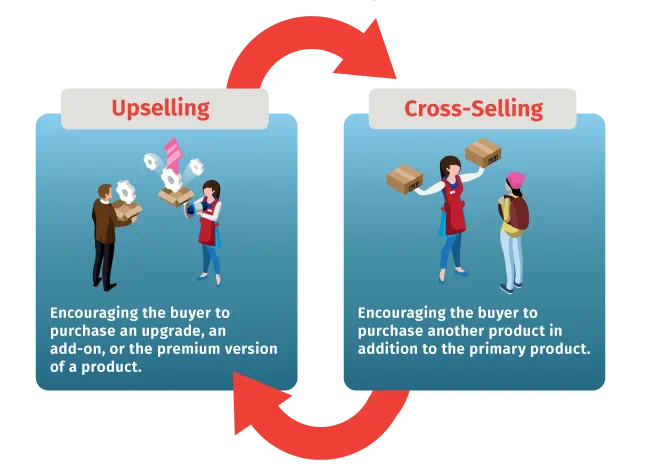
With cross-selling, the seller encourages the buyer to purchase another product in addition to the primary product.
To return to our software sales example, let’s say you offer your customers a volume discount for bundling two products. Using this discount, a customer can purchase two software licenses — ordinarily priced at $50 a month, each — for a total of $80 a month. This nets out to an additional $30 per month or $360 per year for every customer who chooses to bundle. Again, assuming that your existing customer base consists of 10,000 subscribers, if even one out of every 10 subscribers chooses to bundle, you’re looking at an additional $360,000 in revenue per year.
Although sales reps can leverage upselling and cross-selling independently, they generate the greatest returns when used in conjunction. Based on the examples shown above, a sales rep could simultaneously upsell a customer on a product upgrade and cross-sell them a second software license at a discount.
Industry Examples of Upselling & Cross-selling
Upselling and cross-selling apply to any and all industries. Here are just a few examples:
- Manufacturing: While in the process of selling a major piece of equipment to an enterprise-level organization, the sales representative offers the customer additional coverage in the form of an extended warranty.
- Field Service: While performing routine maintenance for a customer, a field service technician notices that another piece of equipment needs repair, if not replacement. The technician uses an app on their mobile device to capture and enter the sales opportunity into the system, including notes and pictures. A sales team member then receives an alert about the potential sales opportunity, assesses the opportunity, and follows up directly with the customer.
- Financial Services: A bank teller pulls up a customer’s profile and, based on householding data, sees that the customer has a child who is nearing college age. Based on this information, the teller sends the customer promotional materials about student checking accounts and student loan options.
- Insurance: While onboarding a new home insurance policy holder, a property and casualty insurance agent notifies the customer that they can lower their monthly rate by bundling home and auto insurance policies.
- Retail: A major clothing company offers automatically generated product recommendations based on previously viewed items and purchases to customers browsing its website.
- Consumer-packaged Goods: Based on customer purchase history data, a CPG company notices that three particular items are frequently bought together. The company decides to offer these items as a bundle to customers as a promotion.
Benefits of Upselling & Cross-selling
Increasing revenue is just one of the many ways in which your business can benefit from upselling and cross-selling. Let’s look at some of the other advantages that upselling and cross-selling offer.
- Upselling and cross-selling can strengthen customer relationships. Upselling and cross-selling aren’t as simple as offering customers the next best version of your company’s product or service or promoting other products from your catalog. Truly effective upselling and cross-selling requires sales reps to have an in-depth understanding of who their customer is, what their goals are, and what’s important to them. Based on this information, reps can tailor their product and service recommendations to the customer’s specific needs.
Naturally, this means that sales reps need to take the time to really to get to know their customers; this level of care and attention not only increases the likelihood of a successful upsell, it also makes customers feel valued and promotes long-term loyalty. To make your sales reps’ jobs easier, invest in a customer relationship management (CRM) system that enables them to store customer information, build detailed customer profiles, and review purchase history.
- Upselling and cross-selling can increase a customer’s lifetime value (LTV). Speaking of loyalty, 57% of customers report spending more on brands or providers to which they are loyal. To that end, upselling and cross-selling not only strengthen relationships and secure loyalty — they can also increase the average order value of each purchase and turn one-time customers into repeat buyers, thereby increasing their LTV. Additionally, using your company’s CRM, you can segment customers based on whether they’ve made upsell or cross-sell purchases in the past and retarget them with new upsell and cross-sell offers.
- Upselling and cross-selling build customer equity. Customer equity is the total combined LTVs of all of your company’s customers. It stands to reason that, given the fact that upselling and cross-selling increase each customer’s LTV, they also increase your company’s customer equity.
- Upselling and cross-selling can grow your business. Not only does selling to existing customers require less effort than working to attract new ones, it also requires less market spend. By simultaneously creating new revenue streams, building customer equity, and decreasing your total marketing spend, you can dramatically increase profits and grow your business that much faster.
- Upselling and cross-selling can enhance your market position. In today’s competitive market, it isn’t enough to say that your products and services are the best in the business — you need to show your work. Similar to how upselling and cross-selling require sales reps to really get to know customers, they also require reps to show customers how your company’s offerings can help them achieve their goals. The most effective way to do this is to support upsell and cross-sell strategies with CRM data. Any CRM system worth its salt will provide full access to campaign analytics, real-time reporting, and easy-to-understand data visualizations that sales reps can use to highlight opportunities and demonstrate to customers how they can benefit from your products and services. This level of insight not only provides full visibility into the value your products and services offer, it also differentiates your business from competitors and can enhance your market position.
How to Successfully Upsell & Cross-sell to Clients
Upselling and cross-selling may be proven, cost-effective ways to increase revenue, but many salespeople leave this money on the table for fear that they lack the necessary skills and coaching. Share these tips with your sales team to help them upsell and cross-sell with confidence:
- Qualify every purchase. Similar to how you would qualify a lead to determine whether they have the potential to become a customer, you also need to vet each order to determine whether it makes practical sense to try to upsell or cross-sell to the customer. The easiest way to qualify a purchase is to ask the following three questions:
- Is the product I’m trying to sell relevant to the original purchase?
- Will the customer benefit from using this product? (And, if so, how?)
- Is the customer open to spending more?
- Know your customer. As we mentioned, truly effective upselling and cross-selling requires a comprehensive knowledge of your customers. In addition to carefully documenting customer information within your company’s CRM, ask probing questions throughout the sales process to get a sense of what matters to the customer and what their needs are. This information will provide valuable context when the time comes to recommend additional offerings.
- Demonstrate value. Don’t just tell customers how great your products are — show them. Whether it’s with a case study, a testimonial, or a customer success story, it’s important to offer real-world examples of how customers can benefit from upgrading or purchasing additional products.
- Limit your recommendations. Upselling and cross-selling is all about being promotional without coming across as pushy. For example, you might be able to think of three different upgrades and four additional products that could be of interest to the customer but decide to present only the three most relevant options to avoid overwhelming them. Remember: Although the ultimate goal is to increase the value of the order, you need to prioritize the customer’s needs above your own.
- Offer incentives. From loyalty perks to product discounts to free trials, incentives can go a long way toward motivating customers to make additional purchases — just be sure to vet any offers through the appropriate channels, first.
- Pitch ideas, not upgrades. The very last thing you want to do is give a customer the impression that you’re trying to get them to spend more money (even if that is, actually, the case). Therefore, it’s important that you frame every recommendation as an opportunity.
Let’s say you work for a company that sells field service software to manufacturers. Rather than tell a customer, “You should consider purchasing the premium version of our solution,” you might say, “I see an opportunity to automate routing and scheduling. Would that be of any interest to you?” To scale back the example a bit, let’s say you’re an associate at a high-end boutique; rather than just tell the customers about different items you have in stock, you might say, “We have a jacket that pairs really well with that blouse.” Upselling and cross-selling are all about helping the customer see the possibilities.
- Start with your most loyal customers. The more loyal the customer, the more likely they’ll be receptive to attempts to upsell and cross-sell. Test out new upsell and cross-sell strategies with your most loyal customers, first, then ask for their feedback on what they think went well and what didn’t. Armed with this information, you can fine-tune your approach to upselling and cross-selling before moving on to new customer segments. That said, be mindful not to overplay your hand — the last thing you want is to turn your company’s most loyal customers into deserters.
- Use technology where possible. Rather than spell this one out here, we’ve decided to dedicate an entire section to it — scroll down to keep reading.
Make Technology a Part of Your Upselling & Cross-selling Strategy
There are any number of ways to leverage technology to support your company’s upselling and cross-selling initiatives. Let’s go over a few examples to give you an idea of what to look for.
- Divide customers into segments. We’ve already touched on this idea, but let’s take a closer look. Customer segmentation refers to the process by which you sort customers into distinct groups — using a CRM system — based on shared characteristics in order to engage in more targeted marketing. Segmentation allows for more granular insight into each customer’s needs, interests, and motivations; using this information, a sales rep can more easily determine what type of upsell and cross-sell strategies and messaging will resonate with the customer.
To take things a step further, a modern CRM solution will also enable your sales and marketing teams to build detailed customer profiles, containing not only each customer’s basic demographic history, but also their purchase history, major life milestones, relational data, and personal preferences for even more personalized upselling and cross-selling.
- Identify your next best offer. Next best offer (NBO), also known as next best action, is a form of predictive analytics that enables marketers and salespeople to gauge which outreach methods — or, in this case, which upsell and cross-sell strategies — are most likely to resonate with customers.
The way it works is this:- You start by defining an objective and a strategy — for example, increasing quarterly sales among your existing customer base by 10%.
- Next, you collect relevant data. Based on the given example, this could be information about customer demographics, buying patterns, product sales, common customer pain points, and so on.
- Now, it’s time to analyze that data in order to glean actionable insights. There are a number of ways to do this, including data segmentation and modeling.
- Based on the findings of your analysis, you implement the NBO and implement the strategies most likely to generate the desired returns. Again, using the given example, let’s say that’s offering some sort of incentive to customers who choose to upgrade their current service offering.
- Repeat the process as needed.
- Conduct product affinity analysis. Product affinity analysis, also known as market basket analysis, is a data mining technique that identifies relationships between purchases and predicts what a given customer or customer segment is likely to purchase next. For example, product affinity analysis may show that a customer who purchased a surfboard is also likely to purchase a wetsuit. It almost goes without saying how upsell and cross-sell strategies stand to gain from product affinity analysis — with a clear sense of what customers are likely to purchase next based on relational data, sales teams can offer more targeted recommendations and increase their chances of closing a deal.
- Leverage machine learning. Certain CRM solutions offer machine learning algorithms for predictive lead and opportunity scoring that can help surface upselling and cross-selling opportunities. Machine learning can also enable sales teams to automatically identify which customers are most likely to purchase additional products and services and capitalize upon those opportunities.
- Develop virtual product catalogs. Make your sales team’s job easier by providing them with a virtual product catalog featuring a full listing of all available offerings, as well as suggested product associations. By storing all product data within a single, centralized repository and offering dynamic related product recommendations, sales reps will be able to more easily identify upsell and cross-sell opportunities and assemble even the most complex quotes for product bundles within minutes.
Drive Sales Excellence with Hitachi Solutions
If you’re interested in implementing these and other technologies to support your organization’s upselling and cross-selling initiatives, Hitachi Solutions is here for you. We have extensive experience with the entire Microsoft suite, including Dynamics 365 Sales Enterprise, Sales Insights, and Customers Insights, as well as our own branded IP built on the Microsoft CRM platform. We’ve also worked with countless organizations across numerous industries, including financial services, CPG, retail, and manufacturing, and have the customer success stories to prove it.
Contact us today to find out how we can help you execute on upsell and cross-sell strategies that drive sales excellence.


