

Customer Data Platforms: Solving the 5 Key Business Challenges in 2023
This comprehensive guide unpacks the potential of Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) in meeting key business challenges, providing you with in-depth case studies, insights on data governance, and a roadmap for responsible AI integration.
Download the WhitepaperIf there’s one thing that consumers in both the B2B and B2C spaces can’t stand, it’s being treated as a monolithic group. The fact of the matter is that even if they’re all shopping for the same product, each and every one of your customers is distinct — they have very different interests, face very different challenges, and have very different needs. Though there may be some overlap, it’s important that you acknowledge and honor each customer’s individuality.
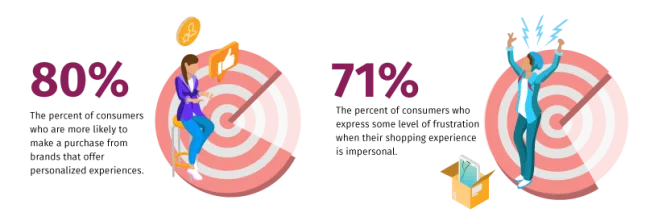
This shift in consumer expectations has led to the rise of personalization. According to research from Epsilon, 80% of consumers are more likely to make a purchase when brands offer personalized experiences. And, according to report from Segment, 71% of consumers express some level of frustration when their shopping experience is impersonal. It’s becoming increasingly clear that personalization is critical to the success of any business, in any industry — and in order to personalize products and services, you must first segment customers.
What is Customer Segmentation?
Customer segmentation refers to the practice of separating customers into discrete groups, or segments, based on shared characteristics, such as age, gender, common interests, or spending habits. Customer segmentation is also known as consumer segmentation or target market segmentation. These segments enable businesses to better understand who their customers are and what matters to them and strategize accordingly.
Customer segmentation is a form of customer analytics. Sometimes referred to as customer data analytics or consumer analytics, customer analytics is the process by which organizations leverage customer data in order to generate meaningful insights and make more informed decisions.
Different Types of Customer Segmentation
- A Priori Segmentation
Customers are grouped based on pre-determined, conventional assumptions rather than empirical market research. - Needs-based Segmentation
Customers are grouped based on shared product and service needs. - Value-based Segmentation
Customers are grouped based on shared economic value. - Demographic Segmentation
Customers are grouped based on shared characteristics, such as age, gender identity, and income. - Geographic Segmentation
Customers are grouped based on what region they live in; this can range anywhere from what town they live in to what country - Technographic Segmentation
Customers are grouped based on their relationship with and attitude towards technology — for example, whether they prefer mobile or desktop, which apps they use, and so on. - Behavioral Segmentation
Customers are grouped based on behavioral patterns, such as how they interact with your brand, how they tend to use products or features, and other frequent actions. - Psychographic Segmentation
Customers are grouped based on shared psychological attributes, such as personality, attitude, beliefs, value, priorities, and motivation. - Customer Journey Segmentation
Customers are grouped based on what stage they are at in the customer journey, such as awareness stage, consideration stage, or decision stage.
The Three Levels of Customer Segmentation
In addition to there being multiple types of segmentation, there are also different levels of segmentation, which are as follows:
- Level One: Manual Segmentation
Relationships managers are responsible for maintaining personal relationships with clients and prospects. Due to the unique level of insight that these relationships offer, relationships managers will oftentimes choose to manually segment customers, or even provide additional context to rule- or query-driven segments. - Level Two: Rule-based Segmentation
By identifying priority segments as an organization, business leaders can establish rules that will automatically segment customers and prospects based on the nature of their relationship with the organization. This method enables the strategic development of prioritized segments in order to identify revenue opportunities, increase wallet share, and identify the right product for the right customer at the right time. - Level Three: Segmentation with AI/Machine Learning
Once it has established rules-based segments, an organization can take segmentation to the next level by supplementing them with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Organizations that leverage AI and ML models can identify and predict a customer’s needs and next actions based on the combined history of all previous interactions with every customer and prospect. A well-executed AI/ML model will contextualize data and signals across multiple different systems.
Why Should You Segment Customers?
We’ve already hinted at some of the reasons why businesses should segment customers — now let’s dig in a little deeper. Customer segmentation offers a wide range of benefits, including:
- More targeted marketing campaigns: Customer segmentation enables you to engage in one-to-one marketing — that is, marketing that leverages individualized messaging to speak directly to the recipient’s interests. You can even develop multiple campaigns, each one designed and directed at a different segment within your larger customer base. This not only satisfies customers’ desire for personalization, but also enables you to allocate marketing spend more strategically.
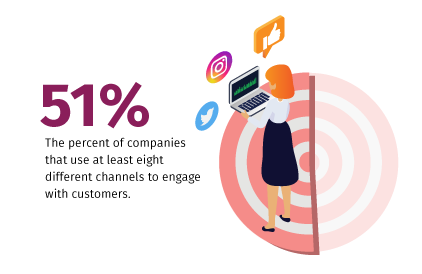
- More effective communication: In today’s omnichannel world, 51% of companies use at least eight different channels to engage with customers. That’s a lot of channels — and not every channel is suited for every customer. For example, one customer may respond best to email communication and another to social media. One of the brilliant things about customer segmentation is that it enables you to drill down into these preferences and devise a communication strategy that’s most likely to get the desired response.
- Product improvements: Customer segmentation gives you a direct view into the challenges your customers face, thereby enabling you to optimize existing offerings or come up with new and innovative solutions to solve those challenges. By looking at things from the customer’s perspective, you identify opportunities for improvement, enhance customer satisfaction, and differentiate your company from competitors.
- Stronger customer relationships: By personalizing every aspect of the customer experience, you can make each customer feel like a valued member rather than just another face in the crowd — and customers who feel valued are more likely to be loyal. Customer segmentation also goes a long way toward making customers feel seen, heard, and understood; taken as a whole, these are the building blocks for a strong, long-lasting customer relationship.
- Superior customer service: Segmentation enhances customer service by providing agents with extensive background information about each customer and valuable context for each interaction. Customer segmentation also enables agents to anticipate customers’ wants and needs, which sets them up to proactively resolve issues and provide more informed support.
- Opportunities to grow revenue: Consumer segmentation supports upselling and cross-selling by providing sales teams with insight into which products, services, and solutions are most likely to appeal to each segment. And that’s just the start: A sales representative can offer even more targeted, granular recommendations by reviewing a customer’s profile, which should include their purchase history, demographic data, personal preferences, and major milestones.
As an added bonus, you can even segment customers by their lifetime value; this enables you to determine which customers are most profitable and channel additional marketing spend to that segment.
A 9-Step Guide to Customer Segmentation
At a high level, the process for segmenting customers consists of three basic stages: gather data, identify patterns, and segment customers. In practice, it’s a little more complicated than that. Let’s walk through the steps.
- Figure out what success looks like. Any time you segment customers, it helps to have a goal in mind. What problems are you attempting to resolve using customer segmentation? What is it that you hope to achieve? What is your desired outcome? Be as specific as you can, using metrics where possible to set measurable goals. By defining what success looks like, you can limit the scope of the project and create alignment with key stakeholders across different business units.
- Establish scope. Speaking of scope, it’s important to set strict parameters for target market segmentation — how many segments you intend to create, what sources you plan to pull data from, and so on.
- Gather data. This one’s pretty self-explanatory — start pulling customer data from your designated internal and external sources to use when building out each segment.
- Define the variables you will use to segment. Segmentation variables are the characteristics you intend to segment customers by, such as demographic traits, geography, behavioral patterns, and so on.
- Validate segmentation variables with key stakeholders. Before you actually start to build out customer segments, check back in with key stakeholders to ensure that their expectations remain the same and that everything is going according to plan.
- Build out customer segments. Finally, the moment we’ve all been waiting for! Again, this one’s pretty self-explanatory.
- Promote internal adoption. Once you’ve created customer segments, you need to make sure that the different business units within your organization actually use them when making strategic decisions. To do so, develop a plan for educating employees and stakeholders alike, share segments with the managers of relevant teams (e.g. Marketing, Sales, Product, Finance), and make yourself available to answer any questions or provide additional guidance, if needed.
- Target your segments. The time has come to put your customer segmentation strategy into play. Start developing personalized marketing campaigns, engaging in targeted sales outreach, and creating other materials tailored to each segment.
- Reevaluate customer segments. Consumer segmentation should be an iterative process. Solicit and review feedback from your various teams on a regular basis to see what’s working (and what isn’t) and make adjustments as necessary. You may even find that you’d benefit from building out additional segments, in which case, you should start this process all over again.
Gain Customer Insights with Hitachi Solutions
Are you ready to start segmenting? Hitachi Solutions can help you leverage the power of Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Insights to start getting results. This enterprise-level customer data platform combines the best in customer relationship management, machine learning, and artificial intelligence technology to unlock insights and drive personalized customer experiences.
And that’s not all — we can even help you establish customer relationships, determine which ones provide the most value, and lend a hand in building out segments based on those relationships. The very best in technology and expertise, combined — that’s the Hitachi Solutions way. Contact us today to get started.


