

Revolutionize Your Customer Insights with Microsoft’s Connected Ecosystem
Don't miss out on this opportunity to revolutionize your customer insights with Microsoft's connected ecosystem
Watch the On-Demand WebinarIncreasing customer expectations and an unsteady economy will create a crossroads for customer experience (CX) programs in 2023. With the potential for companies to start tightening their belts, organizations that have strategies and solutions to improve customer experience — and the data to prove it — will remain healthy and continue to thrive.
Post-pandemic, the idea of what constitutes customer experience was radically re-envisioned for many businesses, as they attempted to create an omnichannel strategy that embraced the best of both the online and in-person experience. Yet many companies still struggle to deliver an exceptional customer experience, and going forward it isn’t going to get any easier.
Fortunately, we’ve put together this primer on customer experience — key performance indicators, best practices, technology and tools— to help provide focus in a time of uncertainty.
What is Customer Experience?
Gartner defines customer experience as “the customer’s perceptions and related feelings caused by the one-off and cumulative effect of interaction with a supplier’s employees, systems, channels or products.” A customer experience (CX) strategy defines how an organization will bring its expression of customer obsession to life as customers engage with them.
These various opportunities for interaction are known as touchpoints, and each touchpoint has the potential to move the consumer further along the customer journey or cause them to disengage entirely. Every touchpoint must be optimized so that, when taken collectively, they create an exceptional end-to-end customer experience. Should a company succeed in achieving this, the business will be rewarded with higher rates of customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy, better word-of-mouth marketing, increased revenue, and so much more.
Customer experience is one of the major points of differentiation a business can make from its competitors and is just as important as cost and product quality. Customers are willing to pay for a better experience, as 84 percent of companies that improved customer experience report an increase in revenue.
What Does an Exceptional Customer Experience Entail?
Every interaction needs to revolve around the concept of individual value, mutual respect, and a shared vision for your future together as their brand of choice.
How does a company clearly demonstrate that to the consumer?
It starts with engagement that is frictionless and convenient, using the channel that makes the customer most comfortable. This means offering multiple channels for communication, such as phone, email, chat, or social media, and ensuring that each channel is staffed by knowledgeable and friendly representatives.
Consumers also want the process of doing business to be simple and straightforward. When issues arise, they want to rectify them in near real-time. Giving customers the resources to figure things out on their own using self-service portals is a great way to do this and will be discussed later in this article.
Then, continuously measure and improve by gathering feedback from customers, tracking key performance metrics, and using that data to make improvements to processes, products, and services.
Tips for Delivering Exceptional Customer Experience
Today’s customers expect companies to understand their needs and tailor their interactions. The elements for delivering an exceptional customer experience may seem obvious, but it’s surprising how many companies fail to adopt them and adopt them consistently. Consider these tips:
- Offer excellent customer service— Ensure that your customers have access to quality customer service, whether it’s through phone, email, chat, or social media. Train your customer service representatives to be knowledgeable, friendly, and responsive to customer needs.
- Provide a personalized experience— Personalization can be key to providing an exceptional customer experience. Use customer data to offer tailored recommendations, promotions, and communications that reflect each customer’s preferences and needs.
- Offer convenient options— Make it easy for your customers to interact with your business. Offer multiple channels of communication, including self-service options such as online ordering, chatbots, and mobile apps.
- Focus on quality— Deliver high-quality products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations. Ensure that your products are reliable, durable, and perform as advertised.
Customer Experience vs. Customer Service
It’s important to specify that customer experience is distinct from customer service. Though important, customer service is only a single opportunity for interaction, specifically the point of interaction where an employee provides a service to a customer.
Customer Service
- It occurs during direct interaction between a customer and a representative of a business.
- Involves the act of supporting or advocating for customers as they inquire, purchase, or troubleshoot a product or service.
- Is usually owned/managed only by a single branch of a business.
Customer Experience
- Encompasses a holistic experience that touches all parts of the company.
- Ranges from the top of the sales funnel to the bottom, from advertisement to personalized follow-up communications.
- Every employee and business representative has an opportunity to improve the customer experience.
Customer Experience vs. Customer Engagement
Customer experience refers to the overall perception a customer has of a company based on their interactions with it across various touchpoints, such as customer service, product quality, and brand messaging. It is a broader concept that encompasses every aspect of the customer’s journey, from initial awareness to post-purchase follow-up.
Customer engagement, on the other hand, refers to the ongoing relationship between a customer and a company. Think of it as a two-way interaction in which both the customer and the company are actively involved. Customer engagement focuses on building deeper connections with customers by encouraging them to participate in activities such as surveys, loyalty programs, social media interactions, and other forms of communication.
Simply, customer experience is the overall impression a customer has of a company, while customer engagement is the ongoing dialogue and interaction between a customer and a company. Both are important for building strong customer relationships and driving business growth.
What Causes Negative Customer Experiences?
When customers receive poor service, it creates a negative experience. These days, customers often take to social media to highlight a poor experience, and unfortunately, it is often seen by others and a company may become viewed as unable to manage simple incidents effectively.
Unresponsiveness, or a delayed response time to a customer service problem, is one type of negative experience that can have adverse repercussions, but it’s not the only one. Consider these examples of common complaints that are often publicized by unhappy customers:
- Poor product or service quality
- Misleading advertising
- Late or delayed delivery of an order or service
- Fees or charges that aren’t transparent during the initial purchase process
- Difficulty getting a refund or exchange
4 Common Customer Experience Mistakes to Avoid
If a company wants to avoid negative social sentiment and the potential loss in customer loyalty and associated revenue, there are a few common mistakes they should avoid:
- Lack of personalization: Failing to personalize interactions with customers can lead to a generic, impersonal experience. This can be avoided by collecting data about customer preferences and tailoring interactions to their needs—this is often called customer segmentation. Personalization is more important than ever for creating a successful experience, and that starts with separating customers into discrete groups based on shared characteristics.
- Inconsistent messaging across channels: If the customer journey is inconsistent across all touchpoints, from in-store to online and mobile devices, When there is no integration between different channels, it can lead to discrepancies in the information provided to customers.
- A complicated purchase process: When customers have to take too many steps, answer too many questions, or repeat themselves during a purchase process, it can lead to frustration and abandon the interaction.
- Forgetting your employees: Empower employees with the right tools and technology so that they can get the job done while ensuring that they have an environment to provide continuous feedback. Unhappy employees won’t provide the individual buy-in necessary to make your strategies effective.
10 Ways to Measure the Customer Experience
There is a wide range of different key performance indicators (KPIs) organizations can use to gauge the health of their customer experience. These KPIs typically vary from one role to the next — for example, a customer service VP is more likely to be concerned about customer satisfaction and customer churn, whereas an IT leader is likely more focused on the total cost of ownership and customers’ service level agreements.
Here’s the list of top customer experience KPIs you should consider tracking. You can download the measurements along with calculations and examples in our infographic.
| KPI | What it is |
|---|---|
| Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) | This KPI indicates overall customer satisfaction with everything from products and services to customer support. |
| Customer Effort Score (CES) | CES — often used in conjunction with CSAT — refers to the amount of energy customers must expend to get an issue resolved, a question answered, or a request fulfilled. |
| Average Handle Time (AHT) | AHT refers to the average time it takes for a call center agent to complete a customer interaction. |
| First Call Resolution (FCR) | FCR is an indication of a call center’s ability to resolve a customer issue or complaint the first time they call in — no follow-up is necessary. |
| Time to Resolution (TTR) | TTR, also known as mean time to resolution (MTTR) and resolution time, refers to the average amount of time it takes a customer service team to resolve a case once it’s been opened. |
| Net Promoter Score (NPS) | NPS evaluates the overall customer experience, customer loyalty, and the potential for business growth. |
| Customer Churn Rate | Customer churn rate refers to the percentage of customers who discontinue services over a given period of time. A high churn rate is a clear indication of low customer satisfaction. |
| Customer Retention Rate | Customer retention rate refers to the percentage of customers that a business retains over a given period of time. Customer retention rate is closely related to customer churn rate. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | CLTV is a prediction of the net profit an individual customer will bring to your company over the course of your relationship (or, alternatively, over a defined period). |
| Customer Equity | Customer equity is a measurement of the total combined lifetime value of all of your company’s customers. |
10 Best Practices for Creating a CX Strategy
Much like Rome, an exceptional customer experience isn’t built in a day — it requires a sustained effort and the flexibility to adapt to changing consumer expectations. But it’s an ongoing critical component to any organization’s ability to handle changing customer expectations and customer loyalty in competitive markets for years to come.
Here’s a primer on some of those best practices:
| Best Practice | Why do it? |
|---|---|
| Define your vision and mission | Develop a framework on which to execute. It’s far easier to create a cohesive customer experience when everyone has a clear idea of what that should look and feel like. |
| Understand what the customer wants and needs | Take a deeper dive to understand what motivates, excites and frustrates customers to understand the degree of changes that have to be made and where they have to be made. |
| Map your customers’ journey | Map where customers might go, as well as traditional paths. The journey is the steps a customer will take to achieve a goal – whether it’s to educate themselves, purchase something, or return a product. It isn’t always linear. |
| Determine how to best capture customer feedback | Secure feedback through as many avenues as possible. Live chat tools, follow-up emails, post-interaction surveys, and outbound calls are all important channels. |
| Target your customers’ emotional motivators | Identify emotional connectors or the feelings that drive a customer’s behavior. What drives a customer to abandon a company or brand? What drives them to become loyal? |
| Craft customer personas | Create representative customer personas for different demographics based on your collected feedback and industry trends. |
| Personalize your customer interactions | Tailor your promotional materials to the individual, connecting with your customers through a combination of customer segmentation and AI. |
| Define a framework for the development of your team | Create the employee experience informed by mixed teams – management, marketing, customer service, designers, etc. This opens communication to provide a more comprehensive perspective. |
Put everything into practice. A customer experience worth talking about has to be consistent across both theory and practice. To motivate everyone to do their very best, business leaders must model a customer-first mindset to their employees. Leadership must also be mindful to incorporate customer-centricity into their company’s guiding principles and to make those principles a key component of new hire training and retraining efforts. In doing so, organizations can create a customer-centric culture that is reflected in the customer experience.
To better practice an exemplary customer experience, consider these steps:
- Adopt CX-centric technology to better collect and analyze customer data.
- Make use of predictive analytics to forecast customer trends.
- Measure your CX levels through a customer metric like the Net Promoter Score.
- Review your ROI after delivering an updated customer experience to determine which areas should be prioritized.
You can download our handy 10 Best Practices for CX Strategy checklist, and keep it nearby as your team creates or reevaluates its CX strategy.
CX Technologies and Tools to Invest in
Every successful customer experience strategy starts with a solid technological foundation. Here are the five tools and technologies an organization needs to craft an exceptional customer experience:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System
A CRM system is the bread and butter of any customer experience strategy and the most vital tool within any organization’s customer experience arsenal. At the risk of stating the obvious, a CRM system is a centralized repository for customer data that enables businesses to gain a better understanding of who their customers are, how they think, and what they want.
By implementing a CRM system, an organization can consolidate data that would be otherwise spread out across many disparate systems, providing it with a 360-degree view of the customer and enabling it to reimagine and redefine the customer experience.
Today’s CRM systems offer robust feature sets and a variety of system integrations for additional extensibility. A cloud-based system like Microsoft Dynamics 365 allows for seamless connectivity between departments, including sales, marketing, and customer service.
One of the more important applications that allows for instant access to this customer data is Dynamics 365’s Omnichannel for Customer Service solutions. Omnichannel solutions provide a holistic view of all your customer-related data gathered from across different channels presented within a unified interface. This ensures that any user will have access to contextual customer information through the most appropriate communication channel. For a closer look at why today’s CX strategy needs to be omnichannel, download our free eBook on Omnichannel Customer Service.
Website [with Self-Service Portals]
It’s generally understood that every business should have a website that consumers can use to learn more about what it does, what products it offers, and who they can contact for more information. The key distinction here is a website with self-service portals.
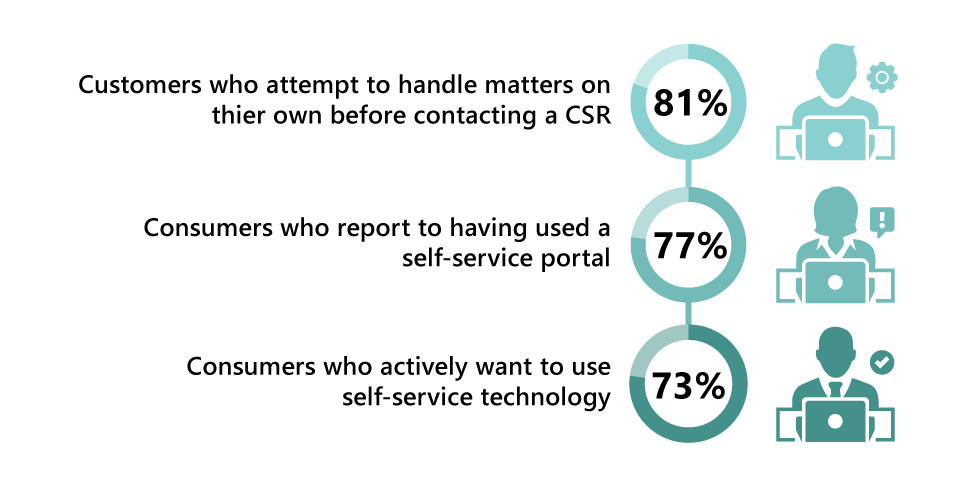
Self-service has become a leading trend in the customer service and support sector in recent years. According to research from the HBR, across all industries, 81 percent of customers attempt to handle matters on their own before contacting a live customer service representative. According to another survey from Microsoft, 77 percent of consumers report having used a self-service portal. It’s easy to understand why: self-service options are fast, easy to use, and convenient, making them ideal for resolving low-level issues.
And customers aren’t the only ones who benefit: By offering self-service options, such as an easily accessible knowledge base and chatbot capabilities, organizations can alleviate the burden placed on call centers, thereby reducing response times, as well as overall spending. Developing self-service solutions may sound daunting, but Microsoft Power Platform applications like Power Apps and Power Virtual Agents allow for the creation of custom tasks and interfaces without requiring a lot of technical know-how.
Referred to as low-code solutions, they allow employees with little to no development experience to create solutions quickly and easily. It can be the answer to improving customer experience and empowering employees at the same time. Take a look at Hitachi Solutions’ opportunity to learn more about low code and how to leverage it to improve the customer experience in your business.
Master Data Management (MDM)
Most organizations generate massive quantities of data on a daily, let alone monthly or yearly, basis. Staying on top of all that data and determining which of it is relevant to enhancing the customer experience requires the assistance of an MDM tool. Master data management refers to the discipline by which businesses ensure accuracy, uniformity, and consistency across all data assets; to that end, an MDM solution is any technology that supports that effort.
MDM solutions are generally used to implement and enforce data entry protocols, remove duplicate data, enrich master data records with information from external data sources, and so on. As far as customer experience is concerned, an MDM solution can bolster a company’s CRM system by ensuring that any data that lives in the CRM is clean and up to date.
Data Analytics
Data analytics software enables businesses to generate meaningful insights from data about everything from customer preferences to buying habits, making it possible for them to anticipate customers’ needs and contextualize the customer journey. Self-service analytics programs like Power BI allow for the creation of interactive, immersive reports.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
A more recent entry into the canon of customer experience technologies, AI is well on its way to becoming a CX staple. There are a wide variety of applications for AI in the realm of customer experience, including intelligent chatbots, personalized product recommendations and marketing campaigns, smart email content curation, automated segmentation, and so on.
Once an emerging technology, AI is expected to dominate the customer experience landscape in the years to come — in fact, according to one prediction, AI will power 95% of all customer interactions by the year 2025.

Incorporating AI into a customer experience strategy can help organizations provide more personalized, efficient, and effective support. For example, sentiment analysis in AI can be used to analyze customer feedback and attitude, providing insights into customer satisfaction levels and areas for improvement. Another use of AI is in predictive analytics, which can be used to analyze customer behavior and identify patterns to predict future actions.
Transform your CX Strategy with Hitachi Solutions
There is a lot to consider when implementing a CX strategy, but that process can be made easier through assessments, workshops, and strategy road mapping on topics tailored to your company’s customer experience needs. Contact Hitachi Solutions today to learn more about these focus areas and to start developing a customer experience strategy that will earn customer loyalty and boost your bottom line.


